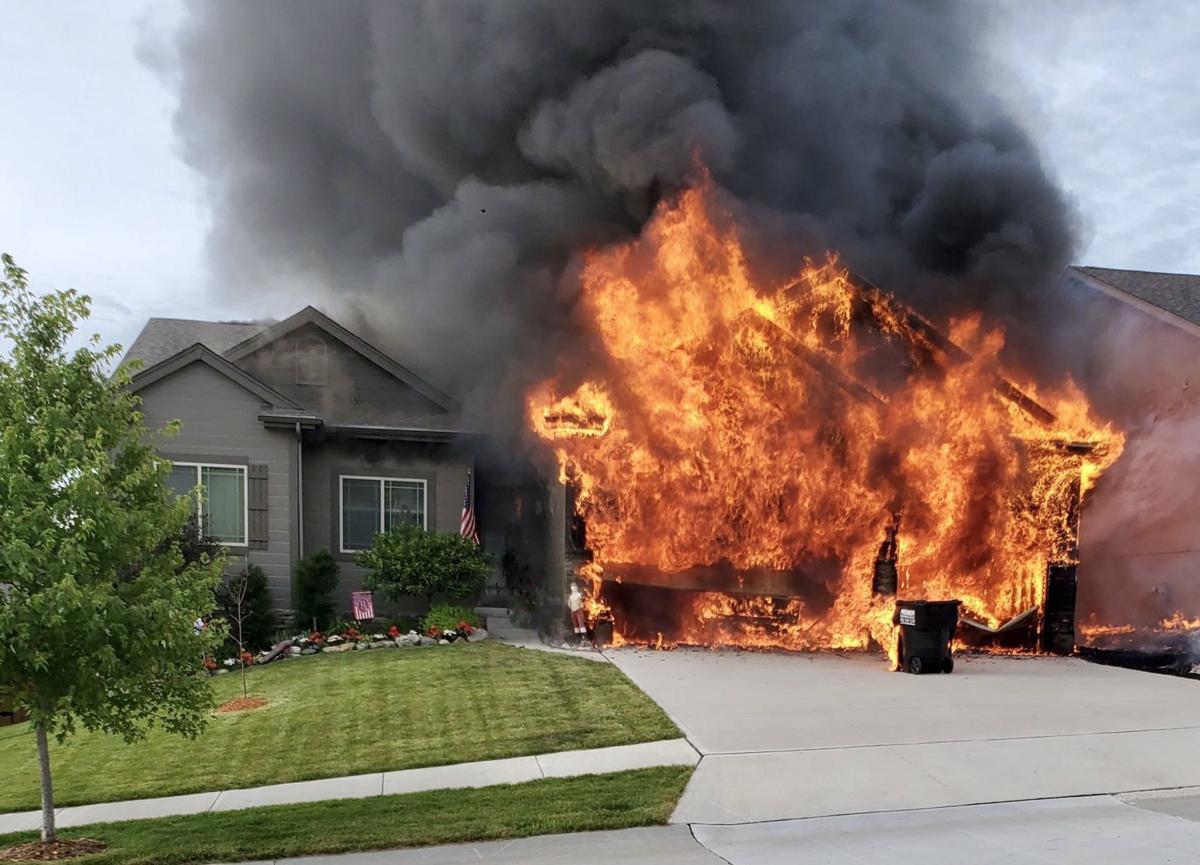
As the new homeowner in 2025, your home is more than just a roof over your head. It is likely to be your most valuable asset, something you likely won’t be able to replace with the limited time and cash in disposal. This is why having insurance for your home with appropriate insurance coverage is important in order to protect and preserve your assets.
What is Homeowners Insurance?
Homeowners insurance coverage is a coverage you purchase to save you from financial problems against certain types of damage to property and against lawsuits. In order to get coverage, you need to pay an insurance company certain amount of money, called a premium. When your premium is paid, you will get protection in return such that as housefire occurs to your property or possessions, the insurance company will compensate you. Homeowners insurance may also give you financial assistance if you accidentally injured someone or cause harm to another people property.
What Does Homeowners Insurance Coverage Cover?
Homeowner insurance coverage protects your home and belongings from accidents such as fires, hailstorms, tornadoes, and broken pipes. If damage is done by one of these incidents, your policy can pay for the repairs. It can also pay you if your belongings are stolen or vandalized.
But a homeowners policy does more than just insure your home and possessions. It can also pay for your attorney if you’re sued, or medical expenses if someone is injured on your property. And if you can’t live in your home following a covered disaster, your policy can pay for a hotel room or rental house while repairs are made.

Basic Home Insurance Coverage Types
There are standard that most homeowners insurance covers including these six types of coverage:
Dwelling Coverage
This coverage covers the physical structure of your dwelling, including walls, floors, windows, and roof. It also usually covers built-in appliances like furnaces and covers attached garages, porches, or decks. Most policies cover your home against loss of any type except those it specifically excludes. The most common reasons for loss claims are wind, hail, freezing, fire, and lightning, the Insurance Information Institute states.
Other Structures Coverage
This homeowner insurance coverage, so the name tells us, provides coverage for other structures on your property that don’t include your main dwelling, such as sheds, fences, or detached garages.
Which losses are insured: Similar to dwelling coverage, most policies insure other structures for any loss except where specifically mentioned otherwise, hence typically insuring losses due to fire, wind, hail, and snow among others.
Personal Property Coverage
Personal property coverage protects your movable items—furniture, clothing, electronics, and non-installed appliances. The majority of policies cover these goods whether in or out of your house. Therefore, if the thief makes off with your bike from outside a store, chances are it is covered (minus your deductible).
Which events are covered: As with dwelling and other structures coverage, which covers any non-excluded loss, not personal property coverage, personal property coverage typically insures against just certain listed events in your policy.
These events, typically called “perils,” typically include:
- Smoke, explotion, fire, lightning.
- Windstorm and hail.
- Theft, riot and vandalism.
- Collapse of snow, sleet, and ice.
- Loss due to an unexpected power surge.
- Volcanic activity.
- Object falling in your property.
- Overflows or discharges of water from household systems.
- Freezing of the aforementioned household systems.
- Sudden bulging, cracking, or rupturing of a fire protection system, hot water, steam, air conditioning, or fire system.
- Damage to aircraft or motor vehicles.
Loss of Use Coverage
Occasionally loss of use coverage can be a real lifesaver if your home becomes uninhabitable due to a covered occurrence. This coverage can pay for hotel stays, meals, or other living expenses while your home is being repaired. If your home is being renovated as a result of a covered claim, loss of use coverage will typically be active. However, if the loss results from a disaster not covered by your policy—e.g., flood—the insurer will not pay for additional living expenses.
Liability Coverage
Liability coverage pays you money if you are responsible for injuring someone or their property. This usually covers all residents of your home, including pets—such as if your dog bites a person at the park, you can be paid. Liability insurance covers the other person’s bodily injury and property damage, with some exceptions. It does not cover criminal offenses, intentional injury, or damages resulting from car accidents (which are the concern of automobile insurance).

Medical Payments Coverage
Also similar to liability coverage, medical payments coverage covers medical expenses if you are involved by accident in causing minor injuries to another individual outside your immediate family. No fault has to be determined prior to the coverage paying out.
Which events are covered: You can use your medical payments coverage if a guest has a minor injury on your property or if you accidentally hurt someone off your property. The same exclusions as liability coverage are used here, except for injuries resulting from intentional acts or car accidents.
What Homeowner Insurance Coverage Won’t Cover
Even the most comprehensive homeowner insurance coverage policy does not insure everything. For instance, you cannot intentionally damage your home and sue your insurance company. Policies typically exclude damage caused by:
- Flooding from external sources like heavy rain or storm surges.
- Drain and sewer backups.
- Earthquakes, landslides, and sinkholes.
- Bird, vermin, fungus, or mold infestation.
- Ordinary wear and tear or neglect.
- Nuclear hazards.
- Actions taken by the government, like acts of war.
- Outages of power.
You can purchase separate coverage for some of these dangers, though. Flood insurance and earthquake insurance are separate policies, and if you are in a hurricane zone, you might also need windstorm insurance.
How Homeowner Insurance Coverage Works:
If your home is completely leveled, your insurance company will not simply cut you a check for the full policy amount. Instead, you will have to file a claim and report the loss. The final payout will depend on your own coverage and deductible.
Replacement Cost vs. Actual Cash Value
One of the deciding points in your settlement is whether your policy will pay the full amount to replace your home—whether that is above your policy limits—or pay actual cash value after depreciation. Some of the choices you might encounter are:
• Actual Cash Value:
This pays the repair or replacement cost of the damaged property less a depreciation deduction. This is usually applied to personal belongings.
• Functional Replacement Cost Coverage:
This pays to restore your house with materials that are comparable but perhaps less expensive, such as substituting plaster walls for drywall.
• Replacement Cost Coverage:
This pays to restore your home with materials of “like kind and quality,” so plaster is substituted for plaster, though the payment won’t exceed your dwelling coverage limits.
• Replacement Cost Coverage for Personal Items:
Some policies offer this option, meaning the insurer will replace your old belongings with new items without a deduction for depreciation, usually at an additional cost.
• Extended Replacement Cost Coverage:
This provides funds above your dwelling coverage limit if the cost to rebuild exceeds expectations, up to a predetermined limit or percentage (for example, 25% above your insured amount).
• Replacement Cost Guarantee Coverage:
This pays for the full amount to rebuild or replace your house after a loss that is covered, even though the expense will be more than your policy would pay. All insurance providers may not offer this.

Homeowner Insurance Deductibles
Homeowners policies commonly have a deductible—the amount that you must pay before your insurer covers the remaining amount. Deductibles might be expressed in terms of:
• A dollar amount, such as $500 or $1,000.
• Some amount of your home’s value insured, like 1% or 2%.
Your deductible is subtracted from your claim payment when you receive it. Choosing a higher deductible usually results in lower premiums but means you’ll pay more out-of-pocket when filing a claim. Conversely, a lower deductible typically comes with higher premiums, but your insurer will cover most of the costs after an incident. Liability claims usually do not have a deductible.
Based on the things above you can look for insurance that cover in many aspect of damages. Also consider cost of premium that you need to paid to insurance company, so that it can help you secure your finance and to to be burden for it. After all things checks out and decide which insurance you will , start to paid premium to maintain the security of your future.