Medicare is a crucial health insurance program that provides coverage for millions of Americans, especially those aged 65 and older, as well as younger individuals with specific disabilities. Whether you’re approaching your 65th birthday or helping a loved one navigate their options, understanding Medicare is essential for making the best choices about your healthcare. In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know—from the basics of Medicare and eligibility to its benefits and cost-saving options.
1. What is Medicare and Who Is Eligible?
Medicare is a federal health insurance program that provides vital healthcare coverage for older adults and certain people with disabilities. It helps reduce the financial burden of healthcare costs, ensuring access to medical care when you need it most.
Who qualifies?
- Individuals aged 65 or older
- Younger people with disabilities or conditions like End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) or ALS (Lou Gehrig’s disease)
- U.S. citizens or legal residents who have lived in the country for at least five years
2. The 4 Essential Parts of Medicare
Medicare is divided into four parts: Part A, Part B, Part C, and Part D. Each part covers different healthcare needs, giving you a range of options to find the coverage that’s right for you.
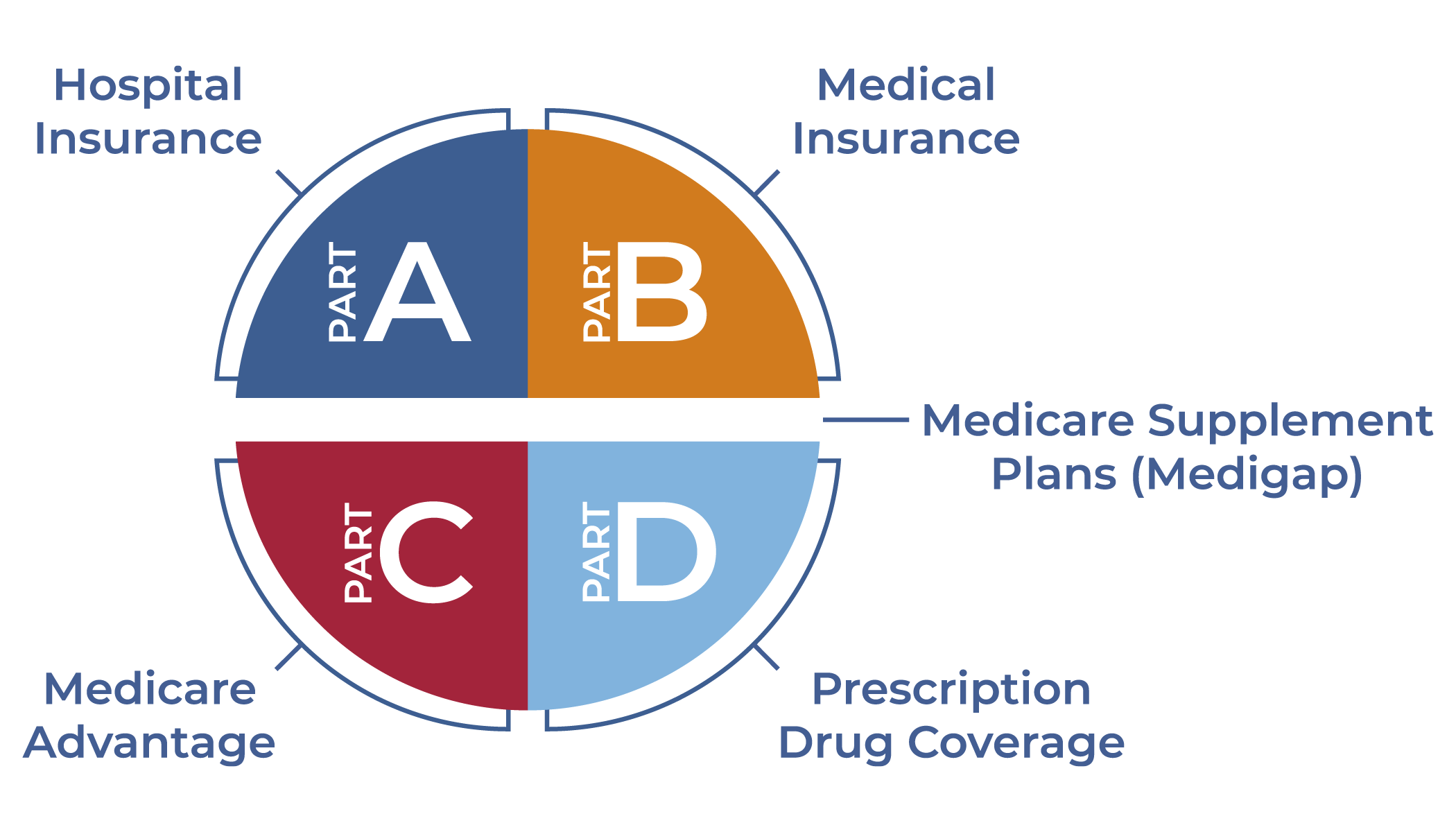
- Medicare Part A (Hospital Insurance):
Covers inpatient hospital stays, skilled nursing care, hospice care, and some home health services. Bonus: Most people don’t pay a premium for Part A if they’ve paid Medicare taxes during their working years. - Medicare Part B (Medical Insurance):
Covers outpatient services, doctor visits, preventive care, and certain medical supplies. It comes with a monthly premium, and you must meet your deductible before coverage kicks in. - Medicare Part C (Medicare Advantage):
An all-in-one alternative to Original Medicare, provided by private insurance companies. Many plans offer extra benefits like vision, dental, and prescription drug coverage. - Medicare Part D (Prescription Drug Coverage):
Helps cover the cost of prescription medications. Part D plans are available through private insurance and have their own premiums, co-pays, and coverage options.
3. How to Sign Up for Medicare
If you’re already receiving Social Security benefits, Medicare will automatically enroll you in Parts A and B when you turn 65. If not, you’ll need to manually sign up. Be sure to watch for your Initial Enrollment Period (IEP), which starts three months before your 65th birthday and ends three months after. Missing this window could result in penalties.

Medicare Enrollment Periods:
- Initial Enrollment Period (IEP): Starts 3 months before you turn 65 and ends 3 months after.
- General Enrollment Period (GEP): For those who miss the IEP, enroll between January 1 and March 31.
- Special Enrollment Period (SEP): If you’re covered by an employer’s plan, you may qualify for an SEP to avoid penalties.
4. Understanding Medicare Costs
While Medicare helps cover healthcare costs, it’s important to be aware of the potential out-of-pocket expenses such as premiums, deductibles, and co-pays. Costs can vary depending on which parts of Medicare you choose and what services you need.
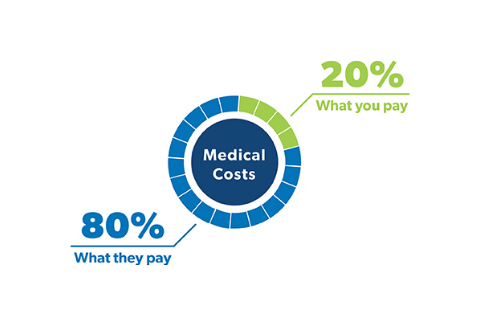
- Part A: Most people don’t pay a premium, but there are costs for hospital stays and other services.
- Part B: Part B comes with a monthly premium (which is income-based), along with deductibles and co-pays.
- Part C and Part D: These private plans vary in cost, depending on coverage options and providers.
5. Extra Coverage Options
Many Medicare beneficiaries opt for additional coverage to help fill gaps in their plans. Consider these options for more complete protection:
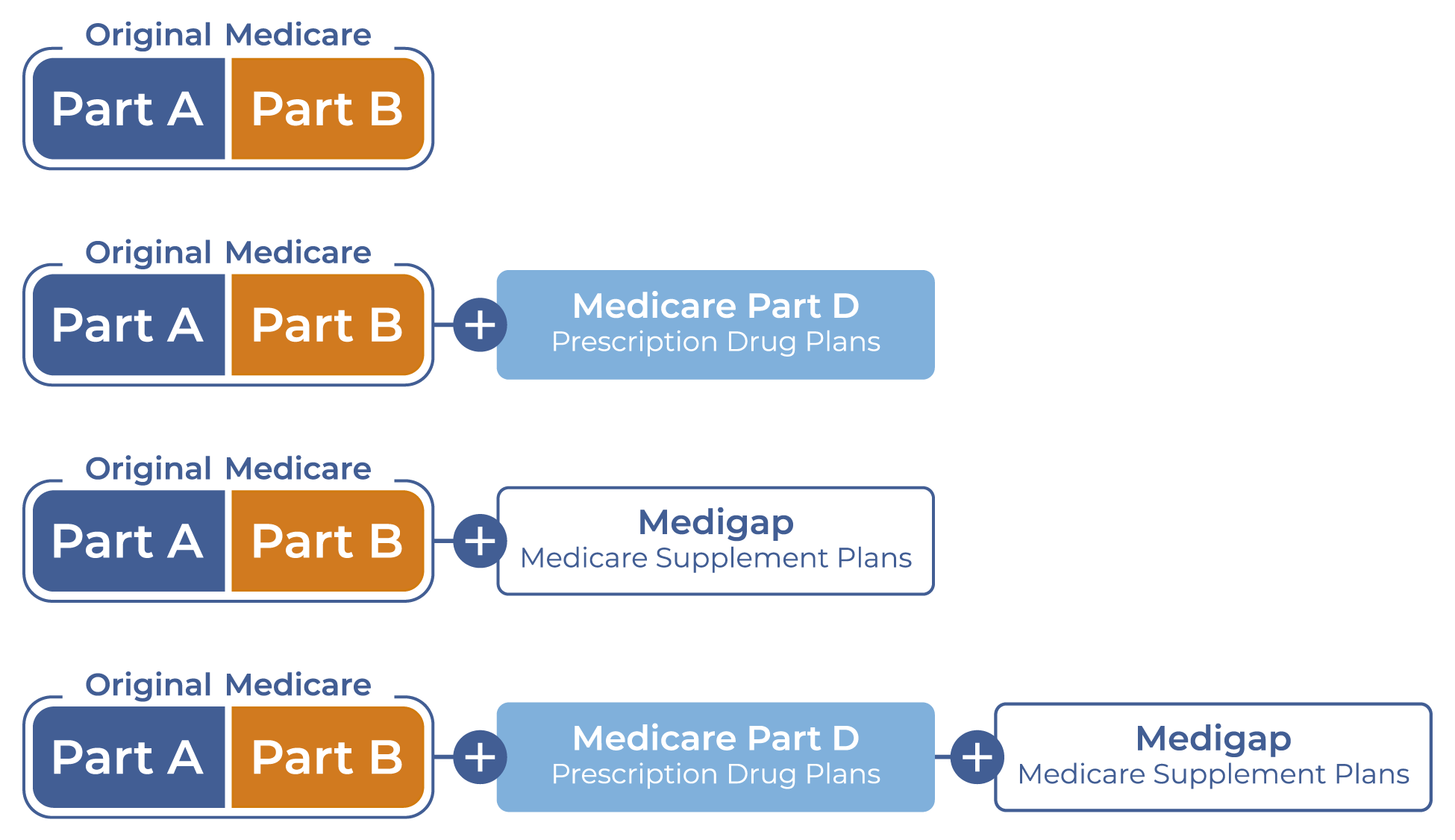
- Medicare Supplement Plans (Medigap): These plans help cover out-of-pocket expenses like co-pays, coinsurance, and deductibles.
- Medicare Advantage Plans (Part C): These all-in-one plans often include additional perks like vision, dental, and wellness programs.
6. Why Choose Medicare? The Benefits Explained
Medicare offers a host of benefits that can significantly improve access to healthcare, including:
- Comprehensive Coverage: Medicare provides coverage for a wide range of services, including hospital stays, outpatient care, and preventive services.
- Prescription Drug Coverage: With Part D, you can manage the cost of medications that are vital to your health.
- Preventive Care: Medicare covers essential preventive services like flu shots, cancer screenings, and wellness visits, helping you stay healthy.
- Customizable Plans: From Original Medicare to Medicare Advantage, you can tailor your coverage to fit your needs.
7. Debunking Common Medicare Myths
There’s a lot of confusion surrounding Medicare, and many myths can make it even more overwhelming. Let’s clear up some of the most common misunderstandings:

- Myth 1: Medicare covers all healthcare expenses.
Fact: While Medicare covers a lot, it doesn’t pay for everything. You may still face out-of-pocket costs, such as co-pays for certain services and drugs. - Myth 2: Medicare covers long-term care.
Fact: Medicare doesn’t cover long-term care like nursing home stays, except under specific conditions. - Myth 3: You must sign up for Medicare at age 65 or face penalties.
Fact: If you have employer coverage, you may be able to delay signing up without penalties. Just be sure to enroll during the Special Enrollment Period if needed.
8. Medicare vs. Private Health Insurance: What’s the Difference?
While Medicare is a government-funded program, private health insurance plans tend to offer broader coverage, especially for working-age adults. Many people choose to combine Medicare with private insurance to get a full spectrum of care. It’s important to evaluate both options carefully to understand which one best meets your needs.
9. Tax Considerations with Medicare
Some aspects of Medicare can impact your taxes. High-income individuals may pay higher premiums for Parts B and D. Additionally, the premiums for Part B and Part D are deducted directly from your Social Security benefits, so it’s essential to understand how this works.
10. Preventing Medicare Fraud
Medicare fraud is a serious issue. To protect yourself, keep an eye on your Medicare statements for errors, report any suspicious activity, and never share your Medicare number with unauthorized individuals.
Conclusion: Why Medicare Matters for Your Health and Wallet
Medicare plays a pivotal role in ensuring that millions of Americans can access the healthcare they need as they age. With its variety of coverage options, including hospital, medical, prescription drugs, and preventive care, Medicare provides comprehensive healthcare support for eligible individuals. By understanding how Medicare works, you can make informed choices about your health insurance and take full advantage of the benefits it offers.